Getting Started with Fundamental Analysis
While the markets can certainly be volatile and unpredictable, one way to navigate this overarching uncertainty can be through using methods like fundamental analysis to help evaluate the value of your trades, and investments, and understand your next steps better.
In this comprehensive beginner’s guide article, you’ll learn how analysis tools work, what fundamental analysis is, how it works, and how to use it. Here’s what you need to know about fundamental analysis:
What Is Fundamental Analysis?
In short, Fundamental Analysis – as the name may suggest – looks into the underlying asset’s fundamental or intrinsic value in order to evaluate and pinpoint trading and investment opportunities. This is because this method can help identify an asset’s future value and growth prospects.
Why Is Fundamental Analysis Important for Traders?
Fundamental analysis can be beneficial to different types of traders since it can help them plan their trading strategies, assess the value of their trades, and predict future price movements. Additionally, it helps traders analyze an asset’s strengths and weaknesses. All of this can help traders navigate volatility and market uncertainty with more ease.
Key Components of Fundamental Analysis
Fundamental Analysis consists of three key components: the health of the economy, the strength of a specific industry, and a company’s financial performance.
Reliable Resources for Fundamental Analysis
Fundamental Analysis focuses on historical data and public data.
- Historical Data: Fundamental analysis looks at historical data, price changes, and patterns in order to analyze future and current trends.
- Public Data: this is especially true when it comes to companies’ stocks. As such, Fundamental Analysis uses public information, which includes companies' earnings, announcements, and news, in order to do the assessment.
Popular Fundamental Analysis Methods
Some of the most popular fundamental analysis tools include looking at economic indicators, analyzing a certain market or industry, and employing valuation techniques.
- Economic Indicators allow traders to evaluate the health of the economy and can, therefore, help them with their decision-making. For example, indicators like Gross Domestic Product (GDP), inflation data, Consumer Price Index (CPI), interest rates, and monetary policy decisions like Central Banks’ announcements among other factors can be helpful. Other indicators that can be referred to include consumer confidence and spending, employment data, and international trade and balance of payments.
- Analyzing a certain industry or market sector can also aid Fundamental Analysis traders as it provides them with an overall picture of that sector and the respective asset. To do so, traders can look into industry-specific metrics and an industry’s life cycle.
- Using valuation techniques involves tools that help gauge the intrinsic value of an asset. These include Earnings per Share (EPS) among other factors and reading financial statements.
Understanding Financial Statements
As mentioned above, one of the most popular Fundamental Analysis tools and methods includes using financial statements, which is especially applicable to stock trading. Financial statements help traders understand where a certain company stands in relation to its peers.
Here’s what you need to know in order to understand financial statements better:
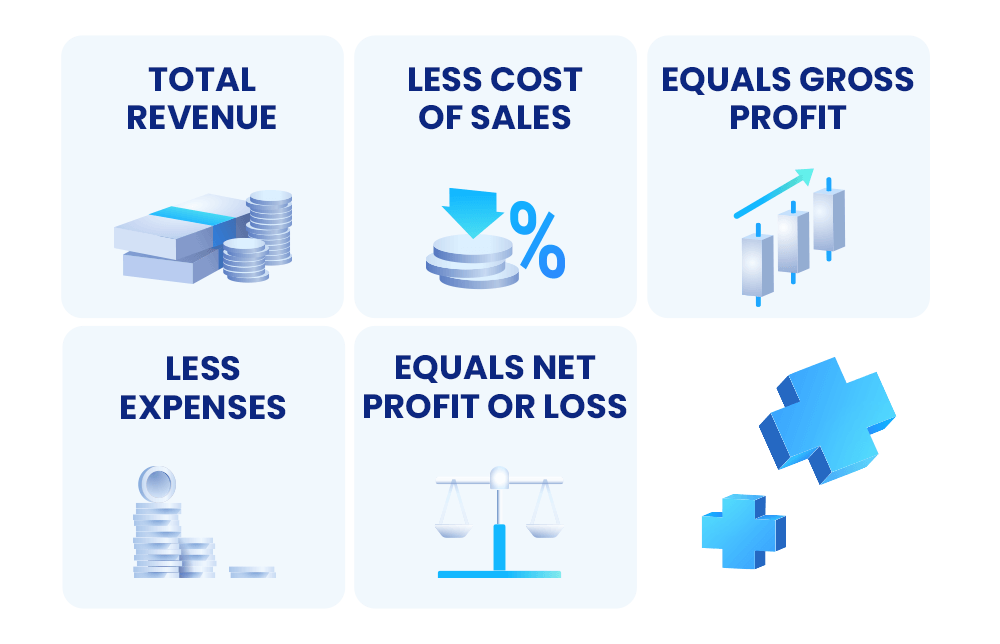
- Balance Sheets: this is essentially an overall statement that shows a company’s financial performance within a certain time period. A balance sheet generally uses this formula:

Furthermore, balance sheets include a company’s assets (cash, inventory, etc.,), liabilities (short-term debt, different revenue, etc.,), and equity (common stock, earnings, etc.). - Income Statement: this refers to a company’s profit or loss which includes its revenue, expenses, gains, and more, and is shared on a quarterly or annual basis.
- Annual Report: this includes public companies’ operational and financial reports like income statements and balance sheets.
- Cash Flow Statement: this serves the essential function of offering a comprehensive overview of a business's cash movements throughout a designated accounting period, thereby showcasing the organization's capacity to sustain its operations in both the short and long run, as determined by the inflow and outflow of cash.
Types of Fundamental Analysis
The two main types of Fundamental Analysis are Quantitative and Qualitative:
- Qualitative: this refers to data that is presented through the quality or nature, i.e. answers questions like why. As such, this type of analysis looks into an underlying asset’s traits or qualities. So, for example, if the underlying asset is a stock, then Fundamental Analysts can look into how consumers approach the company, how it is perceived, and how the company’s management handles decisions.
- Quantitative: this refers to data presented in the form of ratios, numbers, formulas, or figures and discusses the quantity of something. As such, this method uses statistics and reports like a company’s financial statements, quarterly performance, debt, and so forth to assess its performance.
Accordingly, quantitative data tends to be fixed while qualitative data tends to be subjective.
Step-by-Step Guide to Performing Fundamental Analysis
- Look into financial statements in order to examine a company’s current standing.
- Understand what the financial asset is, how it works, and its characteristics.
- Examine a company’s financial performance through periodic earnings reports.
- Keep track of any hurdles or price drops and challenges.
- Understand the asset’s competitors.
- Try to analyze the potential future performance of the underlying asset accordingly.
Trading Psychology and Biased Trading
Equally as important as the other factors, understanding how psychology affects your trading decisions can help you implement your Fundamental Analysis skills better.
This is because when you act on your emotions, you usually end up losing sight of the bigger picture, and therefore, you use your emotions instead of Fundamental Analysis.
In other words, you need to learn how to control your emotions in order to make more informed decisions when trading. To control your emotions and improve your trading psychology, you need to examine and pinpoint your emotions and personal traits and see how you can improve those that hurdle you. In addition, you can create a trading plan in order to set goals and be more specific. Another way to keep your emotions at bay is to base your decisions on research rather than biased opinions.
Conclusion
In summary, fundamental analysis is a crucial tool for traders and investors in the complex world of financial markets. It provides valuable insights by assessing an asset's intrinsic value and growth potential. This analysis relies on economic health, industry strength, and a company's financial performance, all grounded in historical and public data.
Key elements include economic indicators, industry analysis, valuation techniques, and understanding financial statements. Differentiating between quantitative and qualitative data is essential. Additionally, managing trading psychology is emphasized to make informed decisions based on research rather than biases. These insights empower traders to navigate volatile financial markets and improve their chances of success.



