What Is Trading? Definition Guide For Trading
Trading is arguably one of the oldest forms of human interaction and activity and has shaped the landscape of society as we know it today. So what is trading, how does it work and what do you need to become a trader? Here’s what you need to know:
What Is Trading?
Simply put, trading refers to the act of buying or selling financial assets and markets as well as derivatives with the hope of making a profit. A derivative is a tradeable product or contract between 2 or more parties that get their value from financial assets or markets.
The History of Trading
Trading arguably dates back to prehistoric times, with some accounts tracing it to ancient Mesopotamia in 2260 B.C., where humans engaged in the exchange of goods.
However, modern-day trading, as we know it today, and the inception of the first-ever stock exchange can be traced back to the Amsterdam Stock Exchange in 1602.
The Importance of Trading
Trading holds significance not just for traders but plays a vital role in the broader global economy, influencing the labor market by generating job opportunities and impacting economic well-being and global investments. Additionally, it enhances a country's efficiency, fosters foreign direct investments (FDI), and contributes to the growth of various business sectors.
How Does Trading Work?
There are many different types of trading and each one works differently, but overall there’s an overarching explanation of how trading works. Broadly speaking, when trading, the trader opens a trading account with a broker or a trading platform in order to trade certain assets like Forex, Indices, Stocks, or derivatives.
Once the position is closed, if the prices of the asset or derivative align with the trader’s positions, then he or she will gain. Conversely, if the prices of the underlying asset do not align with the traders' positions, then he or she will lose.
Types of Trades - What Assets and Markets Can You Trade?
Depending on the regulation and the jurisdictions, multiple markets and assets can be traded. Here are the main ones:
- Forex: This is the foreign exchange market where currencies are bought and sold (exchanged) based on exchange rates. Examples of Forex pairs include EUR/USD, USD/JPY, and GBP/USD.
- Commodities: This refers to the products or raw materials and goods that are traded. Commodities can range from agricultural like cattle or wheat to energy like oil and natural gas and metals like copper and gold.
- Indices: Indices or indexes are measures of a security or a basket of securities and financial instruments’ prices. Famous examples of indices include the S&P 500, Dow Jones Industrial Average, and the Nasdaq.
- Stocks: Stocks or equities are financial assets that represent a portion of ownership in a company. Stock trading can range from tech to energy sectors and retailers to pharma and aviation.
- ETFs: These are pooled investments that track assets like stocks, indices, bonds, commodities, and currencies. Some examples of ETFs include the SPDR S&P and the iShares Silver.
- Options: Options are derivatives and they grant traders the option to buy or sell the financial asset or market at a predetermined time and price in the future.
Who Can Be a Trader?
To be a successful trader, one needs to possess the following traits (among others):
- The ability to buy or sell financial instruments.
- Mastery of risk mitigation through the use of risk management tools and trading techniques.
- The ability to conduct both quantitative and qualitative assessments. Strong analytical thinking skills.
- The ability to manage one's emotions effectively.
What Does a Trader Do?
Essentially, a trader aims to buy low and sell high to profit from the asset’s or derivative’s price. To achieve this, traders can employ various strategies, such as fundamental analysis or technical analysis, which involve studying an asset’s or derivative’s price charts or intrinsic value to assess whether it may rise or fall.
They then adjust their positions accordingly. Furthermore, traders can consider analyses, news and market events to inform their next moves.
It's also advisable for traders to use risk management tools like stop loss and techniques like hedging to protect themselves from adverse price swings, given the markets' known volatility.
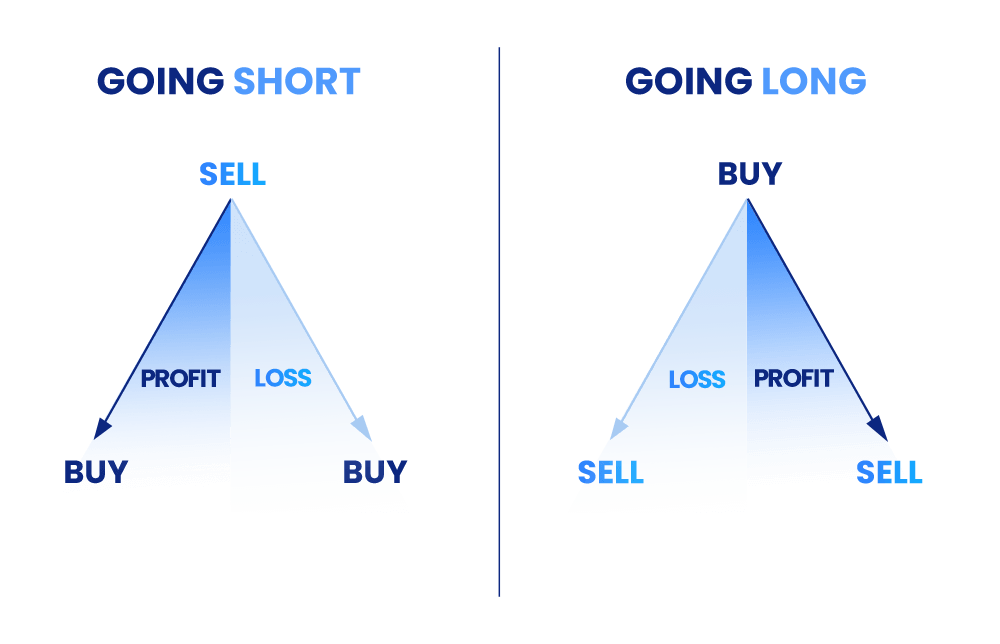
Buy vs Sell - Positions
Buying and selling are fundamental aspects of trading, with buying, also known as taking a “long position”, being a common strategy employed when a trader anticipates a future price increase.
On the other hand, selling, referred to as opening a “short position” or “going short,” occurs when a trader sells an asset or derivative.
CFD Trading
While traders can directly buy or sell a financial asset or market, they may potentially benefit from both rising and falling prices without actual ownership of the asset or market. This can be achieved through buying derivatives such as Contracts for Difference (CFDs), which are offered by companies like Plus500.
CFDs are derivative contracts that allow traders to open buy or sell positions on rising and falling instrument prices without owning the underlying financial asset or market.
These types of contracts are leveraged, which means that if a trade aligns with one's position, traders can magnify their gains. On the flip side, this also means that losses can be magnified if the prices of the asset move against one's position.
Trading Strategy Types
There are many trading strategies available, some of the main ones being Day Trading, Swing Trading, and Position Trading.
- Day Trading: As the name implies, Day Trading involves the exchange of a certain financial assets or derivatives on the same trading day in order to potentially profit from short-term and fast gains.
- Swing Trading: This entails the purchase and sale of specific financial assets, and each trade can span from days to months. Such trading encompasses overnight and weekend risks, prompting traders to typically utilize risk management tools like the risk/reward ratio and stop-loss.
- Position Trading: This form of trading entails identifying specific trends and potential profitable entry points to execute the buying or selling of an asset. The position is maintained until the trend breaks.
You can find out more about each type of trading in our Trader’s Guide article and video titled “Popular Trading Strategies”.
Trading vs. Investing
While trading and investing may often get intertwined it is important to keep in mind that they are, in fact, different actions.
The main difference between trading and investing is that the former is often done in a short period and the latter is done in the longer run.
Therefore, traders might be motivated by short-term profits, whereas investors may have the capacity to endure short-term losses.
Trading Advantages vs. The Risks of Trading
Some of the main advantages of trading may be the potential for profits and liquidity. In addition, this helps with profile diversification as traders gain access to multiple markets.
On the flip side, trading is accompanied by risks of adverse price swings and losses.
What Affects Trading Activity?
Trading activity can either be disrupted or boosted due to negative or positive market sentiment, market conditions, economic changes, monetary policy, volatility, unpredictable events, geopolitics, exchange rates, and supply and demand.
In closing, trading can be profitable but it is also risky. As such, traders and potential traders are encouraged to familiarize themselves with the pros and cons and the strategies involved in it.



