What Companies Are in the S&P 500 & What Moves S&P 500 Prices?
Date Modified: 03/08/2025
The S&P 500 tracks the U.S.'s 500 largest publicly-traded companies by market capitalisation, and is definitely one of the essential market indices. As such, given its importance, many traders and investors may want to keep track of what makes the S&P 500 prices shift, which is covered in this article:

TL;DR
- The S&P 500 tracks the 500 largest publicly traded companies listed in the United States.
- Companies are selected by a committee based on criteria such as market capitalisation, liquidity, and listing exchange.
- The index is weighted by float-adjusted market capitalisation and recalculated every 15 seconds.
- Company earnings, economic data, interest rates, and geopolitical developments are major factors that influence the S&P 500.
- A proprietary index divisor ensures the index's continuity during structural changes.
- Geopolitical events such as wars, trade tensions, and sanctions can significantly impact the index.
- Companies are reviewed quarterly, but selection changes are made cautiously to avoid excessive turnover.
Who Determines the Value of the S&P 500?
The value of the S&P 500 is generated by a company called Ultronics System Corp., which calculates each company's market capitalisation every 15 seconds. This weighted figure is a measurement that traders can use to track the index's performance.
How Do Companies Get onto the S&P 500?
The S&P 500 committee decides which companies to include. The index is often considered to be a stand-in for the U.S. equities market, as it measures the performance of large-cap stocks.
The S&P 500 committee tries to minimise the amount of change that is made to the index's components. While the constituent companies are reviewed every three months, care is taken to avoid too much turnover. The selection criteria are only applied strictly to new additions to the index.
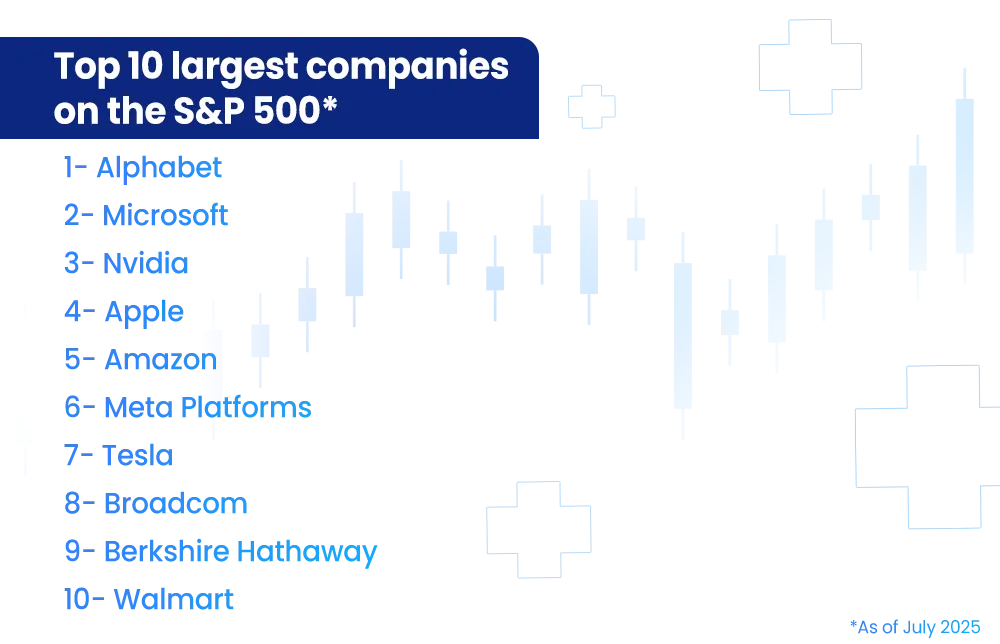
What Are the Top S&P 500 Companies?
- A committee chooses S&P 500 companies based on several factors.
- The rankings are adjusted every quarter. Some of the criteria taken into consideration include the company's market capitalisation, liquidity, domicile, sector classification, and listing exchange.
- Some of the selection criteria are compulsory, such as a market capitalisation of at least US$9.8 billion and a minimum trading volume of at least 250,000 shares per month.
- The companies also need to be traded in the United States and on the NYSE or NASDAQ exchanges, although there are companies on the list that have never been based in the U.S. or were once headquartered in the U.S. but have now moved to other countries.
What Moves the S&P 500's Price?
At the end of each day, the market capitalisations for the companies included in the S&P 500 are calculated. The total float-adjusted market capitalisation of all S&P 500 constituents is then divided by a proprietary index divisor to derive the index's closing value. Due to this methodology, the S&P 500 is heavily weighted towards companies with larger market capitalisations.
Several factors influence the movement of the S&P 500 index:
- Company performance: Earnings per share (EPS), revenue growth, and profit margins.
- Major news: Mergers, acquisitions, scandals, or changes in leadership.
- Economic indicators: Inflation, unemployment, GDP growth, and consumer confidence.
- Interest rates: Decisions by the Federal Reserve can influence investor sentiment and capital flows.
- Index changes: When a company is added to the S&P 500, its share price may temporarily rise due to increased demand from index-tracking funds.
- Float adjustments: The index recalculates to reflect share buybacks or new share issuances.
- Market capitalisation: A company's market cap is calculated by multiplying the number of publicly available shares by the market price per share. The index market capitalisation is the total of all individual company caps.
The index divisor is used to maintain continuity in the index level when structural changes occur, such as stock splits or adjustments to the list of companies included.
How Geopolitics Affects the S&P 500
- Global conflicts: Wars or military escalations can lead to market uncertainty, risk-off sentiment, and downward pressure on the index.
- Trade policies and tariffs: Trade disputes, especially between major economies such as the U.S.and China, can directly affect multinational firms within the index.
- Sanctions and embargoes: Economic sanctions on countries or corporations can harm U.S. companies with global exposure, influencing share prices.
- Political instability: Unrest or regime change in key regions (e.g., the Middle East, Eastern Europe) can disrupt supply chains and commodity prices, affecting sectors like energy and manufacturing.
- Global alliances and treaties: The formation or dissolution of international agreements (e.g., trade deals, climate accords) can alter business conditions and investor sentiment.
- Diplomatic relations: Tensions or improvements in international relations can shape market expectations around global risk, opportunity, and investment flows.
Conclusion
The S&P 500 is one of the most widely tracked indices in the world. It offers a snapshot of the health and direction of the U.S. stock market. It reflects the performance of major corporations and the impact of economic conditions, policy decisions, and geopolitical developments. Understanding what drives the index can help investors make more informed decisions, whether managing personal investments or analysing market trends.
Ready to trade the S&P 500 with Plus500's CFDs? Start here!
*Past performance does not reflect future results.
FAQs
The S&P 500 is a stock market index that tracks the performance of 500 of the largest publicly traded companies in the U.S.
The index is calculated by taking the total float-adjusted market capitalisation of its constituents and dividing it by a proprietary index divisor.
A committee selects companies based on criteria including size, liquidity, sector classification, and trading volume. Reviews occur quarterly.
The largest companies by market cap typically include Microsoft, Apple, Nvidia, Alphabet, Meta, Tesla, and Berkshire Hathaway.
Global conflicts, trade disputes, sanctions, and political instability can affect corporate earnings, supply chains, and investor confidence, influencing the S&P 500's performance.
Yes, as long as they are listed on the NYSE or NASDAQ and meet other criteria, even if they are not headquartered in the U.S.
Changes are reviewed quarterly. The committee aims to limit turnover to preserve the index's stability, only applying strict criteria to new entrants.
Learn More About S&P 500
Related News & Market Insights
Get more from Plus500
Expand your knowledge
Learn insights through informative videos, webinars, articles, and guides with our comprehensive Trading Academy.
Explore our +Insights
Discover what’s trending in and outside of Plus500.
Stay up-to-date
Never miss a beat with the latest News & Markets Insights on major market events.


