Cocoa Trading Guide: What Is Cocoa and How to Trade It?
Date Modified: 12/10/2025
Cocoa is commonly associated with chocolate, one of the world’s sweetest delights, but its significance extends beyond mere sweetness, impacting the economy at large and the commodity market in particular. Here’s what you need to know about cocoa trading:

TL;DR
- Cocoa beans are agricultural commodities that refer to the seeds grown on the Theobroma cacao trees in the Amazon rainforest
- Cocoa is mainly grown in tropical regions around the equator like Ghana and the Ivory Coast
- Cocoa is harvested by opening ripe pods and fermenting the beans
- Cocoa can be traded with CFDs or Futures contracts
What Is Cocoa?
Cocoa, the cocoa seed, or the cocoa bean is a type of fermented seed that grows on the Theobroma cacao tree (a small evergreen tree) native to the Amazon rainforest.
In the commodity market, cocoa refers to an agricultural commodity that can be traded in various ways.What Is the Meaning of the Word Cocoa?
Trading agricultural goods can be achieved through Agricultural Futures contracts as you can open buy or sell contracts that obligate you to buy or sell the underlying commodity at a preset price and date in the future.
The Origins of the Cocoa Bean
Cocoa, first encountered in the rainforests of South America, has held significant cultural importance in Central America, notably within the Mayan civilization, where cocoa trees were revered and referred to as the “Food of the Gods.”
Where Is Cocoa Grown?
The cocoa bean thrives in tropical climates, particularly surrounding the Equator, with the majority of the cocoa trees being grown in Ghana and the Ivory Coast.
Statistics from Statista.com show that in 2023 about 70% of the world’s cocoa stemmed from these West African countries.
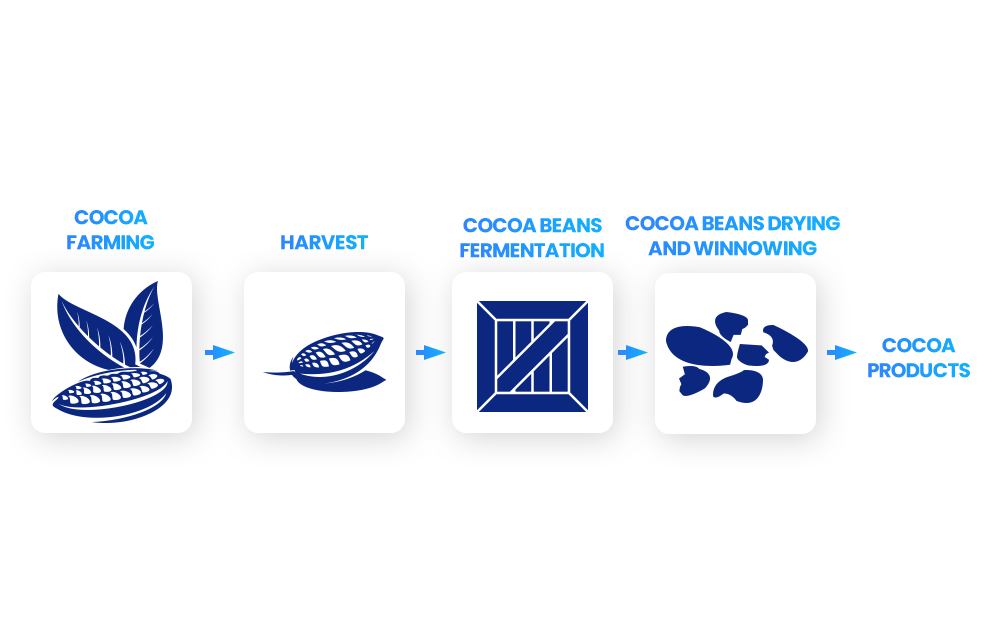
How Is Cocoa Harvested?
Cocoa is harvested from the branches of the cocoa tree by removing ripe pods, opening them, and then extracting the wet beans.
It takes 10 days to open the pods after harvesting, after which they are grouped together and either split or fermented.
What Drives Cocoa Prices?
A variety of factors can affect the price of cocoa, with the main ones being climate change, geopolitics, consumer sentiment, currency fluctuations, public health, human rights, and—yes, you guessed it—demand for chocolate, cocoa's primary product.
Climate Change
Perhaps unsurprisingly, cocoa is directly affected by climate conditions. For example, deteriorating climate conditions in West Africa, where cocoa is primarily grown, have proven to be damaging to cocoa crops, leading to a drop in production. This, in turn, caused cocoa prices to surge in 2023 as supply decreased while demand for cocoa continued to rise.
Geopolitics
Geopolitical tensions can also play a role in driving the cocoa prices.
Take, for example, the Russia-Ukraine war which began in February 2022 and caused energy commodity prices, like oil and gas, to surge on supply concerns. This not only had an impact on energy commodities but also affected cocoa prices.
European chocolate producers were worried that they couldn’t run their factories, causing them to order fewer cocoa. However, once these manufacturers realized they could continue their operations, they began competing over a limited cocoa supply, causing cocoa prices to soar and subsequently drop as Europe is known to be the world’s biggest cocoa importer.
Additionally, the war also caused fertilizer prices to soar, resulting in less usage, and driving cocoa prices upward due to limited supply.
Market Sentiment
Simply put, market sentiment refers to how positively or negatively market participants view a certain market sector or instrument. In other words, it refers to how bullish or bearish traders, investors, and analysts are.
Generally speaking, when sentiment is bullish on cocoa, it is likely to drive its price upward. Conversely, when sentiment is bearish or negative, it is likely to push cocoa's price downward.
Currency Fluctuations
Since cocoa is traded all around the world and predominantly priced in either US dollars or British pounds (sterling), fluctuations in these currencies can directly impact the value of cocoa by altering the competitiveness of cocoa-producing nations.
Public Health
As health trends evolve and awareness of the potential effects of chocolate and sugary sweets grows, the price of cocoa can fluctuate.
For instance, when concerns about the health impacts of chocolate gain prominence, cocoa prices tend to decrease due to a drop in demand for chocolate.
Human Rights
Concerns about the low labor costs in cocoa production can impact cocoa prices, particularly if human rights are breached, leading to potential disruptions in cocoa production and subsequent price fluctuations.
Demand for Chocolate
Given the fact that cocoa is the main ingredient in chocolate-making, both chocolate and cocoa share a symbiotic relationship.
This is because higher demand for chocolate leads to increased demand for cocoa, which, in turn, can drive up cocoa prices. On the flip side, lower chocolate demand reduces the need for cocoa, potentially resulting in lower cocoa prices.
Additionally, it's worth noting that high cocoa prices can sometimes pose profitability issues for chocolate manufacturers like Hershey’s, for example, as they may cause chocolate prices to soar, subsequently leading to a drop in consumer demand.
You can find out more about what can drive commodity prices, in general, in our article titled “What Are the Main Drivers of Commodity Prices?”
It is important to keep in mind that while the aforementioned factors can affect cocoa prices, past performance does not reflect future results.
How to Trade Cocoa
Given cocoa’s surging demand, many traders and investors may be interested in gaining exposure to the cocoa price changes.
While there’s a myriad of ways available to trade cocoa, one of the most commonly used ones is through Futures contracts or Contracts for Difference (CFDs):
Cocoa Futures
Cocoa Futures are derivative contracts between two parties stipulating that they must exchange cocoa (the underlying commodity) at a predetermined price and date in the future.
Cocoa Futures are traded on Futures exchanges like the New York Mercantile Exchange or London’s Intercontinental Exchange.
Cocoa Futures are traded in New York between 4:45 AM and 1:30 PM (04:45 - 13:30), in London between 9:45 AM and 6:30 PM (09:45 - 18:30), and in Singapore between 5:45 PM and 2:30 AM (17:45 - 02:30).
*please note that the plus500 trading hours may vary and are listed in the instrument details on the trading platform.
Cocoa Contracts for Difference (CFDs)
Cocoa (CC) CFDs are derivative contracts between two parties, typically a buyer and a seller or a trader and a CFD provider, allowing them to trade the difference in the price of cocoa from the initiation of the contract until its closure without physically owning it.
This type of cocoa trading enables traders to potentially profit from both rising and falling cocoa prices, depending on their position and the market's direction. Additionally, cocoa CFDs are leveraged*, meaning that both gains and losses can be magnified.
To find out more about CFD trading, check out our video and article titled “What Is CFD Trading?”
More Ways to Trade Cocoa
Cocoa can also be traded through Options, ETFs, Spread Betting, or through trading the shares of chocolate-producing companies like Nestle (NESN.VX) or Mondelez (MDLZ) for example.
Trading Cocoa CFDs with Plus500
If you feel like cocoa CFD trading is the right choice for you, you can do it with Plus500 through the following steps:
- Open a trading account.
- Log into the platform using either the web app or the mobile app.
- Search for cocoa by entering it into the search bar, or navigate to the commodity category on the left side of the screen and select cocoa.
Alternatively, you can open a free and unlimited Demo Account to practice trading cocoa CFDs under real market conditions without risking your actual capital. You can continue doing so until you feel confident enough to trade cocoa CFDs in real mode.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Cocoa Trading
Before embarking on your cocoa trading journey, it is important to understand the pros and cons of this agricultural commodity.
Some of the potential advantages of cocoa trading include the fact that there are multiple ways to trade it, catering to the diverse trading needs and styles of traders.
Additionally, cocoa is known for its volatility, making it a suitable option for both position traders and day traders.
On the other hand, cocoa can be influenced by various factors, which may make it less desirable for traders seeking a more stable portfolio.
Conclusion
To conclude, cocoa's significance transcends its association with chocolate, impacting global economies and commodity markets.
While trading cocoa offers opportunities, it also comes with risks. As such, understanding these dynamics is essential for potential traders.
FAQs
Cocoa is mainly grown around the equator and thrives in tropical regions. As of 2023, the majority of global cocoa production comes from West Africa from countries like Nigeria, Ghana, the Ivory Coast, and Cameroon.
Originally, the cocoa tree is native to upper Amazon regions like Brazil, Peru, and Colombia.
Cocoa is globally regulated by the Federation of Cocoa Commerce (FCC) and the Cocoa Merchants’ Association of America (CMAA) in the USA.
Related News & Market Insights
Get more from Plus500
Expand your knowledge
Learn insights through informative videos, webinars, articles, and guides with our comprehensive Trading Academy.
Explore our +Insights
Discover what’s trending in and outside of Plus500.
Stay up-to-date
Never miss a beat with the latest News & Markets Insights on major market events.